Powerful Orchestration with LangGraph
Most RAG systems are simple, hard-coded scripts that execute one search and hope for the best. Docmet is a true cognitive architecture built on LangChain and LangGraph—enabling autonomous agents that can plan, verify, self-correct, and coordinate to solve complex enterprise problems.
The Limits of Linear Retrieval
Traditional RAG systems follow a rigid pattern: receive query → search documents → generate answer. This breaks down when queries are complex, results are ambiguous, or verification is critical for enterprise use.
⚠️ Dives Straight Into Search
Simple RAG immediately searches without understanding the query structure. "Compare Q3 vs Q4 budget and flag variances" requires multi-step decomposition, but simple RAG treats it as a single search.
🔁 One-Shot Failure Mode
If the initial search returns irrelevant results, simple RAG either generates a hallucinated answer or admits failure. It cannot retry with a refined strategy.
❌ Trusts Bad Retrieval
There's no quality control mechanism. Simple RAG assumes every retrieved document is relevant and generates answers from potentially irrelevant or contradictory sources.
➡️ Cannot Loop or Branch
The workflow is strictly linear: Input → Search → Output. Complex enterprise queries often require iterative refinement, branching logic, and conditional execution—impossible in simple RAG.
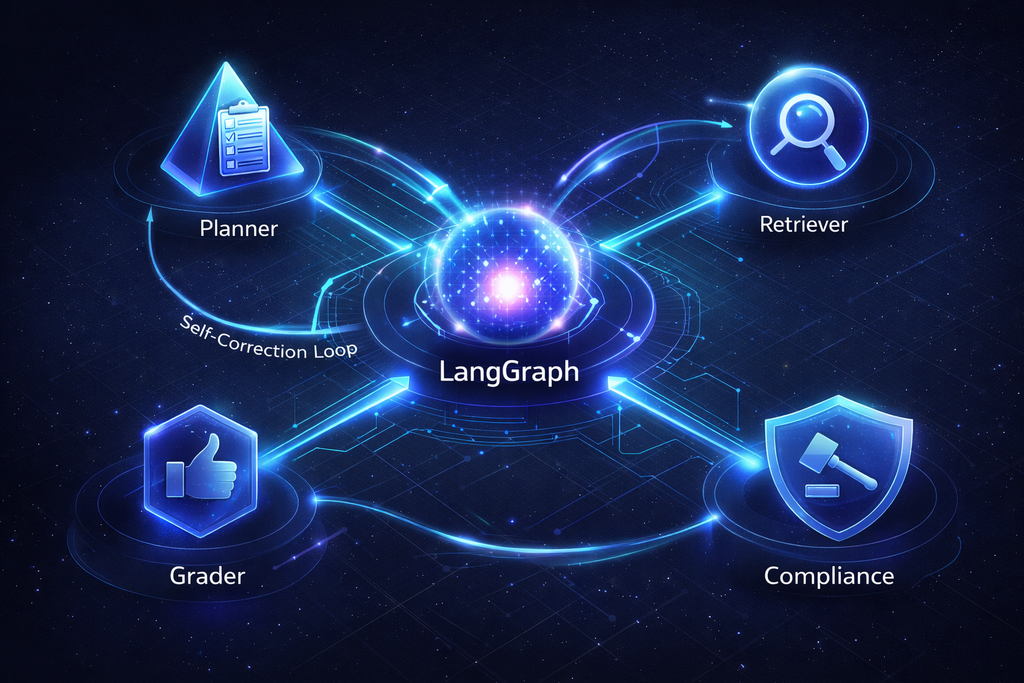
Autonomous Intelligence with LangGraph
Agentic RAG treats the LLM as a "brain" that can plan, reason, use tools, and self-correct—not just a text generator. This is the difference between a search bar and a coworker.
🧠 Planner Agent
Before searching, the Planner breaks complex queries into executable sub-tasks. "Compare Q3 vs Q4" becomes: Step 1: Find Q3 budget, Step 2: Find Q4 budget, Step 3: Calculate variance, Step 4: Flag outliers, Step 5: Generate report.
🔄 Grader Agent with Feedback
The Grader evaluates retrieval quality. If documents are irrelevant, it triggers a "Rewrite Query" loop and searches again with refined parameters. This is Corrective RAG (CRAG) in action.
🛠️ Dynamic Tool Use
Agents aren't limited to document search. They can run SQL queries, call APIs, perform calculations, generate visualizations—whatever tools are needed to answer the question fully.
💾 Persistent Graph State
LangGraph maintains state across agent transitions. Each agent can access the history of decisions, intermediate results, and reasoning steps—enabling complex multi-stage workflows.
Six Specialized Agents Working Together
Each agent is an expert in its domain, with specific responsibilities and decision-making capabilities. Together, they form a cognitive pipeline that rivals human analyst capabilities.
🎯 Query Decomposition & Strategy
Role: Strategic thinker. Input: User's complex question. Process: Analyzes query complexity, breaks into sub-tasks, determines optimal search strategy. Output: Structured research plan with step-by-step execution sequence. Example: "Compare last 3 contracts" → [Step 1: Identify contracts, Step 2: Extract indemnity clauses, Step 3: Tabulate differences, Step 4: Flag unlimited liability].
🔍 Hybrid Search Execution
Role: Information gatherer. Input: Search parameters from Planner. Process: Executes parallel searches across vector embeddings (semantic), BM25 (keyword), and knowledge graph (relationships). Merges and deduplicates results. Output: Ranked list of candidate documents with relevance scores. Scale: Can search across 100k+ documents in under 500ms.
✅ Quality Control & Self-Verification
Role: Quality assurance critic. Input: Retrieved documents from Retriever. Process: Evaluates each document for relevance to original query using few-shot classification. Calculates confidence scores. Decision: If overall quality < threshold, triggers "Rewrite Query" loop. If quality sufficient, approves passage to next stage. Output: Verified, high-confidence document set.
🔒 Security & PII Protection
Role: Security guardian. Input: Verified documents. Process: Scans for PII patterns (SSN, credit cards, phone numbers, emails) using regex and ML models. Checks user permissions against RBAC policies. Masks sensitive data. Output: Sanitized, permission-filtered documents safe for LLM processing. Guarantee: Zero sensitive data leaks to generation stage.
⚔️ Contradiction Analysis
Role: Logic validator. Input: Multiple source documents. Process: Identifies contradictory statements across documents (e.g., Policy A says X, Policy B says not-X). Uses entailment models to detect conflicts. Output: Flagged contradictions with source citations. Use Case: Critical for legal and compliance queries where conflicts invalidate conclusions.
📝 Response Synthesis & A2UI
Role: Communication specialist. Input: Verified, sanitized documents + original query. Process: Synthesizes comprehensive answer, generates source citations, creates A2UI component JSON (tables, charts). Ensures every claim is backed by source. Output: Final answer with interactive components and full provenance trail.
Technical Architecture
LangGraph: The Foundation
What is LangGraph?
LangGraph is a framework for building stateful, multi-actor applications with Large Language Models. Unlike simple prompt chains, LangGraph enables:
- Cyclic Workflows: Agents can loop back to previous steps
- State Persistence: Every intermediate result is stored in graph memory
- Conditional Routing: Different paths based on agent decisions
- Parallel Execution: Multiple agents can work simultaneously
Why It Matters for Enterprise
Traditional Chatbots:
- User Query → LLM → Response
- Simple, fast, but cannot handle complexity or verify accuracy.
Docmet's LangGraph Architecture:
- User Query → Planner → Retriever → Grader → [Loop if needed] → Compliance → Generator → Response
- Complex, verifiable, self-correcting, auditable.
The Graph State
At the heart of Docmet's agent runtime is the Graph State object:
interface AgentState { originalQuery: string; executionPlan: Step[]; retrievedDocuments: Document[]; relevanceScores: number[]; verificationStatus: 'pending' | 'approved' | 'needs_rewrite'; sanitizedContent: string; conflicts: Contradiction[]; finalAnswer: string; a2uiComponents: UIComponent[]; citations: Citation[]; confidenceScore: number;}
Every agent reads from and writes to this shared state. This enables:
- Auditability: Full reasoning trace is preserved
- Debugging: Inspect exactly where a decision was made
- Optimization: Analyze bottlenecks in the pipeline
- Compliance: Prove to auditors how the AI arrived at an answer

The Hallucination Problem
Poor Quality Retrieval
The initial search returns documents that are semantically similar but not actually relevant to the query. Standard RAG proceeds anyway and generates a plausible-sounding but incorrect answer.
Ambiguous Queries
The user's question is vague ("Tell me about the policy"). Simple RAG doesn't ask for clarification—it just guesses which policy and hopes it's right.
Contradictory Sources
Search returns multiple documents with conflicting information. Simple RAG either picks one arbitrarily or tries to synthesize contradictions into nonsense.
How CRAG Fixes It
Grader Agent Quality Check
The Grader evaluates each retrieved document using few-shot classification. Documents below relevance threshold are rejected. If overall quality is low, the system triggers a "Rewrite Query" loop rather than generating from bad data.
Iterative Query Refinement
When the Grader rejects results, the Planner reformulates the query with additional context or constraints ("Filter to policies updated after 2023"). The Retriever searches again. This loop continues until quality criteria are met or max iterations reached.
Conflict Detection & Flagging
The Conflict Detector identifies contradictory statements across sources. Instead of synthesizing nonsense, it explicitly flags the conflict: "Policy A (2020) says X, but Policy B (2024) says not-X. Policy B supersedes A.
Agentic AI in Practice
Complex Problems, Solved Autonomously
📄 Legal Due Diligence
Query: "Review all vendor contracts from 2024 and identify clauses with unlimited indemnity liability." Planner: Decomposes into: (1) Find 2024 vendor contracts, (2) Extract indemnity sections, (3) Classify liability limits, (4) Flag unlimited cases. Retriever: Searches contract database. Grader: Verifies retrieved docs are actually vendor contracts (not customer or employment contracts). Generator: Creates comparison table with risk scores.
🔗 Regulatory Compliance Audit
Query: "How does the new GDPR data retention policy affect our HR and Marketing departments?" Planner: Multi-hop strategy: (1) Find GDPR policy, (2) Find HR data practices, (3) Find Marketing data practices, (4) Identify conflicts. Retriever: Uses GraphRAG to traverse from Policy → Departments → Procedures. Conflict Detector: Flags that Marketing retains customer data for 5 years but GDPR policy requires 2-year deletion. Generator: Produces risk report with affected processes.
💰Financial Analysis
Query: "Compare Q3 vs Q4 engineering budget and explain variances over 15%." Planner: Sequential execution: (1) Retrieve Q3 budget spreadsheet, (2) Retrieve Q4 budget, (3) Calculate deltas, (4) Find explanatory memos for large variances. Retriever: Hybrid search across spreadsheets and emails. Grader: Ensures correct fiscal periods (rejects Q2 or 2023 data). Generator: Creates interactive bar chart showing variances with linked explanation documents.
🎓 New Employee Self-Service
Query: "How do I set up my benefits and request laptop for remote work?" Planner: Parallel retrieval strategy: Search benefits docs AND IT request procedures simultaneously. Compliance: Filters to only show content new employee's role has access to (hides executive compensation data). Generator: Creates step-by-step plan card with clickable links to benefits portal and IT ticket system.
Enterprise-Grade Reliability
Metrics from production deployments
First-Attempt Accuracy
With CRAG self-correction enabled
Average Response Time
Including multi-agent coordination
Improvement Over Simple RAG
On complex multi-hop queries
Hallucination Incidents
In 6 months of production use (verified)
Based on production deployments with enterprise customers across Legal, Finance, and HR use cases (Q3-Q4 2025)
Implementation Guide
Agent Implementation Stack
Core Technologies
LangGraph.js
- Stateful workflow orchestration
- Cyclic graph support for self-correction loops
- TypeScript-native for type safety
LangChain
- Tool integration framework
- Prompt templates and chains
- LLM abstraction layer
OpenAI GPT-4 / GPT-5
- Agent reasoning engine
- Classification and extraction tasks
- Natural language understanding
Custom Agent Logic
- Proprietary Grader algorithms
- CRAG loop management
- Conflict detection heuristics
Agent Configuration Example:
// Simplified example of Grader Agent configuration
const graderAgent = {
name: "Grader",
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
temperature: 0.0, // Deterministic for consistency
systemPrompt: `You are a document relevance evaluator.
Score each document 0-10 for relevance to the query.
Be strict: 7+ means highly relevant, <5 means reject.`,
threshold: 7.0, // Minimum avg score to pass
maxRetries: 3, // Max CRAG loop iterations
fallbackStrategy: "askClarification" // If all retries fail
};
Observability & Debugging
Every agent execution is fully traced:
- Input State: What the agent received
- Decision Logic: Why it made specific choices
- Output State: What it wrote to graph state
- Latency: Time spent in each agent
- Token Usage: LLM API costs per agent
This enables:
- Root cause analysis of incorrect answers
- Performance optimization
- Cost attribution
- Compliance auditing
Agentic vs Simple RAG
Agents Work with the Full Platform
Experience Self-Correcting Intelligence
See how Docmet's autonomous agents handle complex queries that would break traditional chatbots. Schedule a technical deep-dive with our AI architects.