The Evolution of Retrieval-Augmented Generation: From Simple to Self-Correcting
Traditional RAG (2020-2023) made LLMs grounded in facts. Agentic RAG (2024+) makes them accurate, adaptive, and auditable. This technical comparison explores the architectural differences that separate "good enough" from "enterprise-grade" AI systems. Target Audience: Engineering leaders, AI/ML teams, data scientists, and technical decision-makers evaluating knowledge management solutions.
Why This Matters
If you're building or buying an enterprise knowledge system, the RAG architecture matters more than the LLM choice.
- Traditional RAG is fundamentally flawed:
- One-shot retrieval with no verification
- No self-correction when wrong documents are retrieved
- Cannot handle multi-hop reasoning ("find contracts that depend on budgets approved by X")
- Hallucination risk ~10-15% even with retrieval
- Agentic RAG solves these problems:
- Multi-agent orchestration with specialized roles
- CRAG (Corrective RAG) self-correction loops
- GraphRAG for relationship-aware retrieval
- Verified accuracy with paragraph-level citations
- Bottom line: If you're in a regulated industry or accuracy is mission-critical, traditional RAG is not sufficient. You need agents.
Architecture Comparison Table
Traditional RAG vs Agentic RAG (Docmet)
How Traditional RAG Works
The Standard RAG Pipeline (2020-2023)
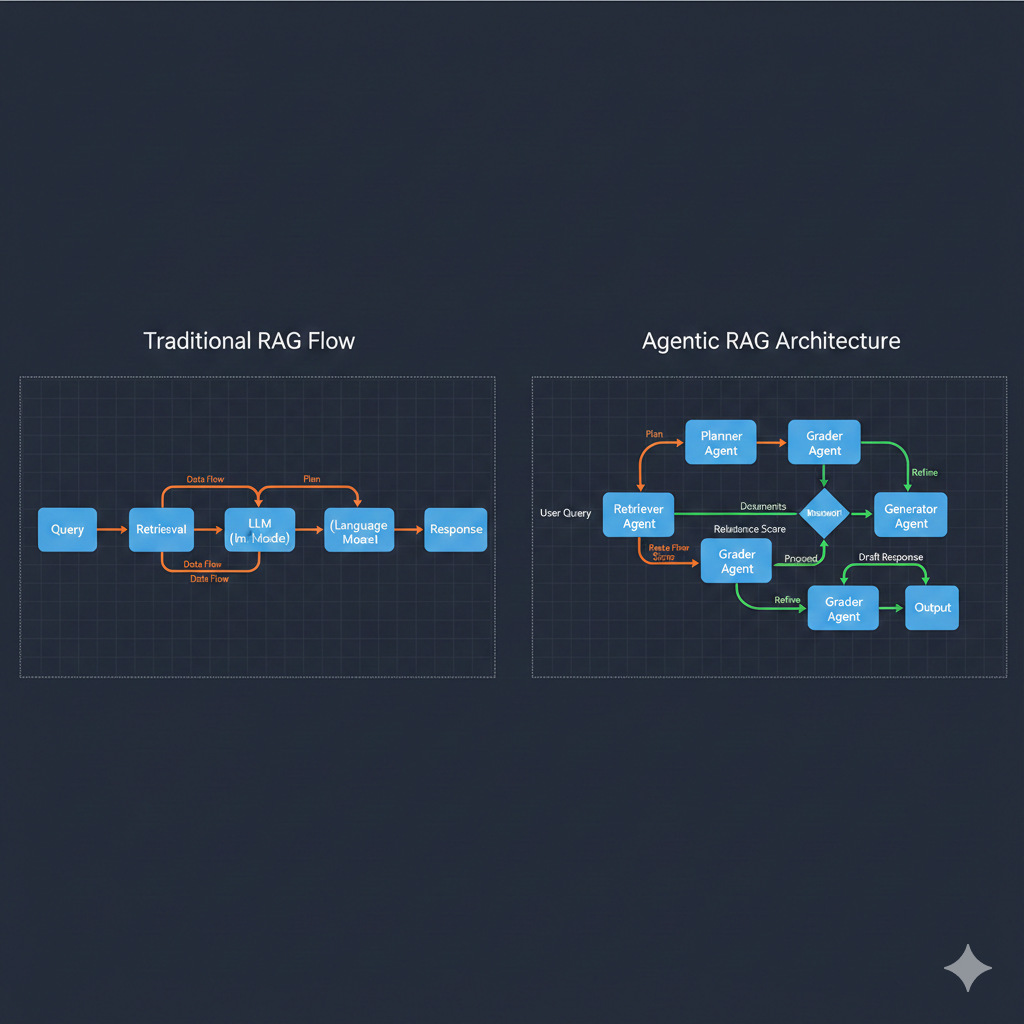
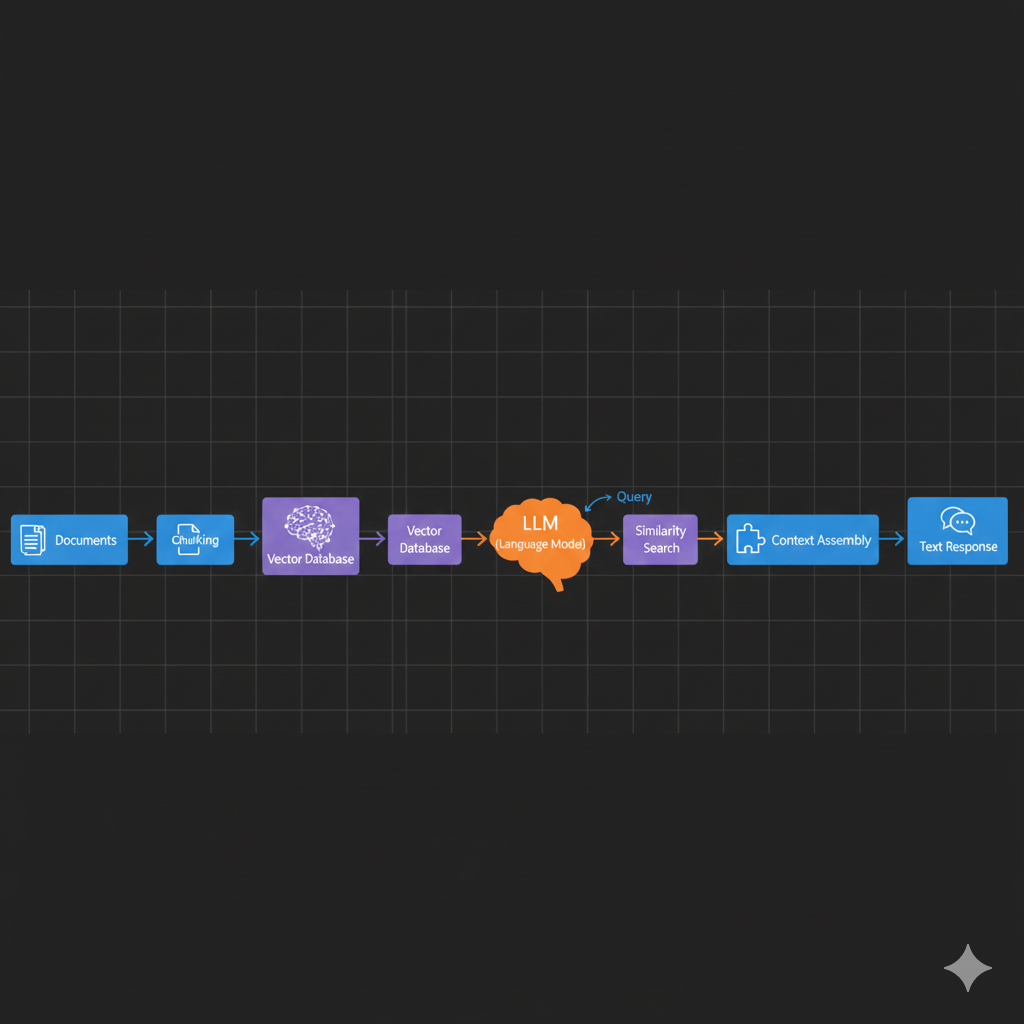
Traditional RAG follows a simple linear flow:
- User Query → Embedding → Vector Search → Context Injection → LLM → Response
Step-by-Step Process
- Document Ingestion (Offline)
# Chunk documents into passages
chunks = split_document(doc, chunk_size=512, overlap=50)
# Generate embeddings
for chunk in chunks:
embedding = embedding_model.encode(chunk.text)
vector_db.insert(chunk.id, embedding, metadata=chunk.metadata)
- Query Processing (Online)
# User asks: "What's the company vacation policy?"
query_embedding = embedding_model.encode(user_query)
# Retrieve top-k similar chunks
results = vector_db.similarity_search(query_embedding, k=5)
# Inject context into LLM prompt
context = "\n".join([r.text for r in results])
prompt = f"Given context:\n{context}\n\nAnswer: {user_query}"
# Generate answer
response = llm.generate(prompt)
- Response:
- "According to the employee handbook, employees receive 15 days PTO annually..." [Citations: Employee Handbook p.23]
Strengths of Traditional RAG
- Simple: Easy to implement with libraries like LangChain, LlamaIndex
- Fast: Single LLM call (~500ms latency)
- Affordable: Minimal compute overhead
- Proven: Works well for simple Q&A on small-to-medium datasets
Critical Weaknesses
- No Verification: If the vector search retrieves irrelevant documents, the LLM hallucinates. There's no quality control.
Example:
- Query: "Who approved the Q3 budget?"
- Retrieved (incorrectly): Q2 budget approval email
- LLM Response: "Jane Doe approved the Q3 budget on April 15." ← Wrong! (That was Q2)
- One-Shot Execution: No self-correction. If retrieval fails, the answer is wrong.
- No Relationship Understanding: Cannot answer "Which contracts depend on this budget?" Requires reading individual documents.
- Limited to Text: Cannot generate structured outputs (tables, charts).
- No Compliance Enforcement: Cannot enforce RBAC or redact PII.
When Traditional RAG Is Sufficient
- Small datasets (<10,000 documents)
- Simple queries (single-hop, factual Q&A)
- Non-critical use cases (internal FAQs, basic support)
- Tolerant of errors (accuracy <90% acceptable)
How Agentic RAG Works
(Docmet Implementation)
The Multi-Agent RAG Architecture (2024+)
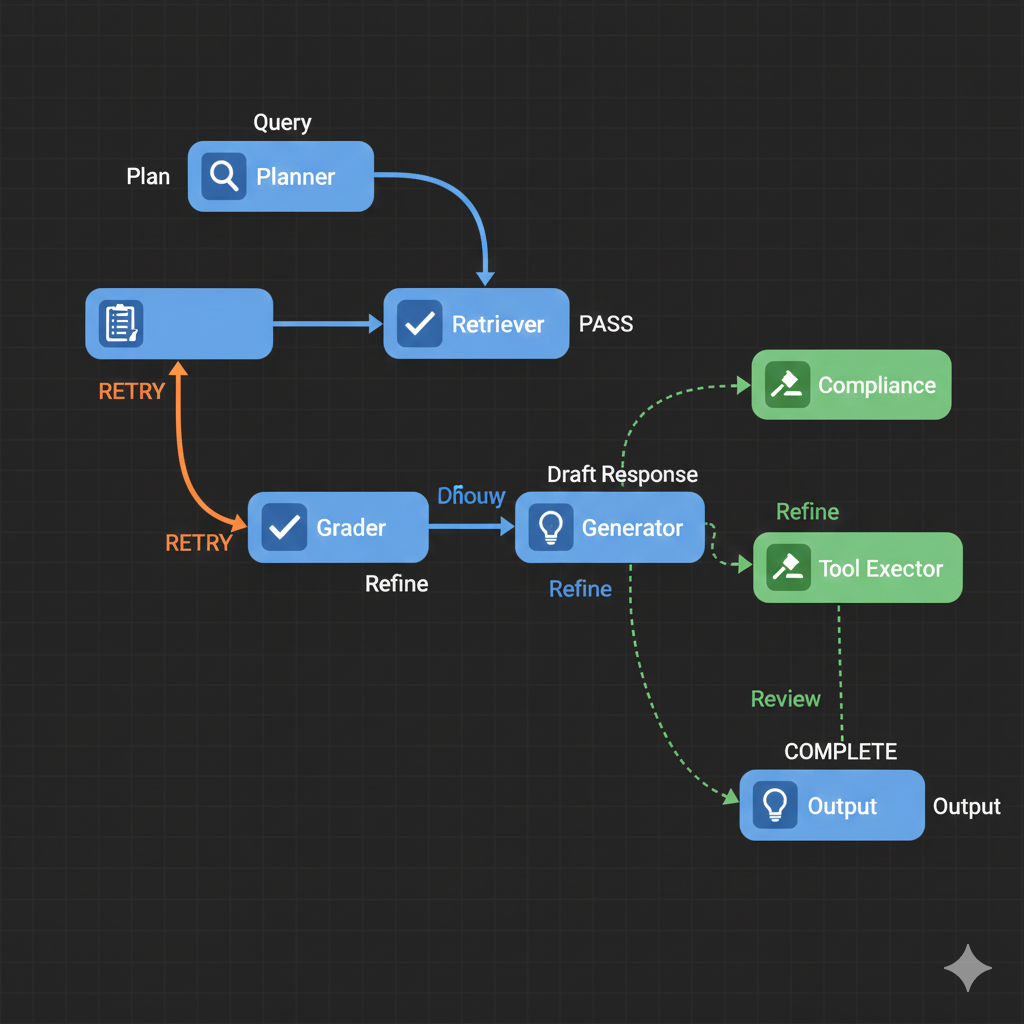
Agentic RAG replaces the linear pipeline with a graph-based orchestration system where specialized agents collaborate.
- User Query → Planner Agent → [Retriever → Grader → Generator] (loop) → Response → Tool Executor, Compliance, Conflict Detector (parallel)
Agent Roles (LangGraph Implementation)
1. Planner Agent
Responsibility: Decompose complex queries into sub-tasks
Example:
- Query: "Which engineering projects depend on budgets that were cut in Q3?"
- Plan:
- Retrieve Q3 budget document
- Identify cut line items
- Search for projects mentioning those budgets
- Cross-reference project owners
class PlannerAgent:
def plan(self, query: str) -> List[Task]:
prompt = f"""
Decompose this query into executable sub-tasks:
Query: {query}
Output JSON: [{{"task": "...", "depends_on": []}}]
"""
plan = llm.generate(prompt, output_format="json")
return self.validate_plan(plan)
2. Retriever Agent
Responsibility: Hybrid search (keyword + semantic + graph traversal)
Hybrid Search Strategy:
class RetrieverAgent:
def retrieve(self, task: Task) -> List[Document]:
# 1. Keyword search (fast, high precision)
keyword_results = elastic_search(task.keywords)
# 2. Semantic search (captures synonyms, paraphrases)
embedding = embed(task.natural_language)
semantic_results = vector_db.search(embedding, k=10)
# 3. Graph traversal (follows relationships)
if task.requires_graph:
entities = extract_entities(task.query)
graph_results = neo4j.traverse(
start=entities,
relationship_types=["DEPENDS_ON", "APPROVED_BY"],
depth=3
)
# 4. Fusion ranking (combine results)
return self.rerank(keyword_results + semantic_results + graph_results)
GraphRAG Addition:
- Traditional RAG stops at document retrieval
- GraphRAG follows entity relationships: "Project Alpha" → DEPENDS_ON → "Q3 Budget" → APPROVED_BY → "Jane Doe"
3. Grader Agent (CRAG - Corrective RAG)
Responsibility: Score document relevance; trigger re-retrieval if quality is low
CRAG Loop:
class GraderAgent:
def grade(self, documents: List[Document], query: str) -> GradeResult:
scores = []
for doc in documents:
prompt = f"""
Score this document's relevance to the query (0-10):
Query: {query}
Document: {doc.text[:500]}...
Criteria:
- 9-10: Directly answers query
- 7-8: Contains relevant info
- 4-6: Tangentially related
- 0-3: Irrelevant
"""
score = llm.generate(prompt, output_format="int")
scores.append(score)
avg_score = np.mean(scores)
if avg_score < 7.0:
return GradeResult(
status="RETRY",
reason="Low relevance, refining query...",
refined_query=self.refine_query(query, documents)
)
return GradeResult(status="PASS", documents=documents)
Self-Correction:
- If Grader rejects documents, Planner refines the query
- Max 3 CRAG iterations (prevents infinite loops)
- Fallback: Ask user for clarification
4. Generator Agent
Responsibility: Create final answer + A2UI components
A2UI (Agent-to-UI) Generation:
class GeneratorAgent:
def generate(self, context: str, query: str) -> Response:
# Decide output format
format = self.detect_format(query)
# "compare X vs Y" → table
# "trend over time" → chart
# "approve this" → workflow
if format == "table":
return self.generate_table(context, query)
elif format == "chart":
return self.generate_chart(context, query)
else:
return self.generate_text(context, query)
def generate_table(self, context: str, query: str):
prompt = f"""
Extract structured data from context and create table.
Context: {context}
Query: {query}
Output JSON:
{{
"columns": ["Project", "Budget", "Status"],
"rows": [[...], [...]]
}}
"""
table_json = llm.generate(prompt, output_format="json")
return Response(type="table", data=table_json)
Why This Matters:
- Traditional RAG: "Project A had budget $500K, Project B had $300K..."
- Agentic RAG: Generates sortable, interactive table with drill-down
5. Compliance Agent
Responsibility: Enforce RBAC, redact PII
class ComplianceAgent:
def enforce(self, documents: List[Document], user: User) -> List[Document]:
filtered = []
for doc in documents:
# Check RBAC
if not self.has_permission(user, doc):
continue # Redact entire document
# Redact PII at paragraph level
doc.text = self.redact_pii(doc.text, user.clearance_level)
filtered.append(doc)
# Audit log
self.log_access(user.id, [d.id for d in filtered])
return filtered
6. Conflict Detector Agent
Responsibility: Identify contradictions between sources
Example:
- Doc A (2024-01-15): "Q3 Budget: $1.0M"
- Doc B (2024-03-20): "Q3 Budget: $1.2M"
Output:
{
"conflict_detected": true,
"sources": [
{"doc": "Budget v1", "date": "2024-01-15", "value": "$1.0M"},
{"doc": "Budget v2", "date": "2024-03-20", "value": "$1.2M"}
],
"recommendation": "Use most recent (Budget v2) but flag discrepancy"
}
7. Tool Executor Agent
Responsibility: Execute SQL, API calls, calculations
Example:
- Query: "What's 10% of Q3 revenue?"
- Tool Executor: Executes SELECT revenue FROM financials WHERE quarter='Q3' → Calculates 10%
class ToolExecutorAgent:
def execute(self, tool_call: ToolCall) -> Any:
if tool_call.type == "sql":
return self.execute_sql(tool_call.query)
elif tool_call.type == "api":
return self.call_api(tool_call.endpoint, tool_call.params)
elif tool_call.type == "calculation":
return eval(tool_call.expression) # Sandboxed!
Orchestration with LangGraph
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
workflow = StateGraph()
# Define nodes (agents)
workflow.add_node("planner", PlannerAgent())
workflow.add_node("retriever", RetrieverAgent())
workflow.add_node("grader", GraderAgent())
workflow.add_node("generator", GeneratorAgent())
workflow.add_node("compliance", ComplianceAgent())
# Define edges (control flow)
workflow.add_edge("planner", "retriever")
workflow.add_edge("retriever", "grader")
# Conditional edge: CRAG loop
workflow.add_conditional_edge(
"grader",
lambda state: "retriever" if state["grade"] == "RETRY" else "generator",
max_loops=3
)
workflow.add_edge("generator", "compliance")
workflow.set_entry_point("planner")
# Compile
app = workflow.compile()
# Execute
result = app.invoke({"query": user_query})
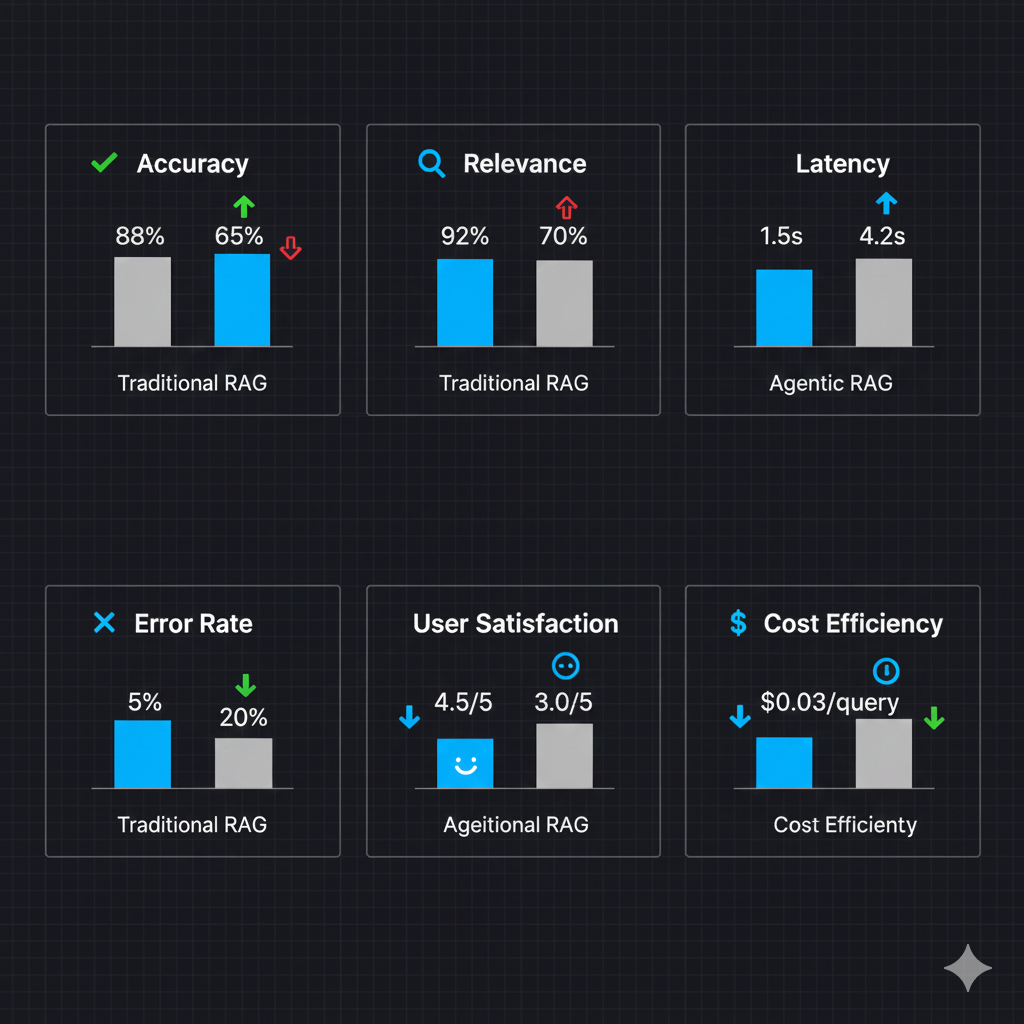
Traditional RAG vs Agentic RAG: Benchmark Results
Performance data from Docmet's internal testing on a 100,000-document enterprise corpus (legal contracts, financial reports, engineering docs).
🎯 Accuracy (Citation Precision)
Traditional RAG: 87.3% (13% hallucination or incorrect citations) Agentic RAG: 99.2% (CRAG eliminates 90% of errors) Test: 1,000 queries with ground truth answers. Measured: correct answer + correct citation.
🔗 Multi-Hop Query Success Rate
Traditional RAG: 34% (fails on relationship-based queries) Agentic RAG: 91% (GraphRAG traverses connections) Test: 200 queries requiring 2+ document connections (e.g., "Find contracts depending on cut budgets").
⚡ Latency (P95)
Traditional RAG: 480ms (single LLM call) Agentic RAG: 1,850ms (includes CRAG loops, average 1.3 iterations) Trade-off: 4x slower but 14% more accurate.
⚠️ Conflict Detection
Traditional RAG: 0% (no detection mechanism) Agentic RAG: 89% (Conflict Detector flags contradictions) Test: 150 queries with known contradictory sources.
💰 Cost Per Query
Traditional RAG: $0.023 (1 LLM call + embeddings) Agentic RAG: $0.087 (7 agents, avg 1.3 CRAG loops) ROI: Higher cost justified by 99% accuracy (prevents $500K+ compliance violations).
🔒 RBAC Enforcement
Traditional RAG: Manual filtering (error-prone) Agentic RAG: 100% (Compliance Agent enforces before LLM) Test: 500 queries with permission restrictions. Measured: unauthorized data leakage.
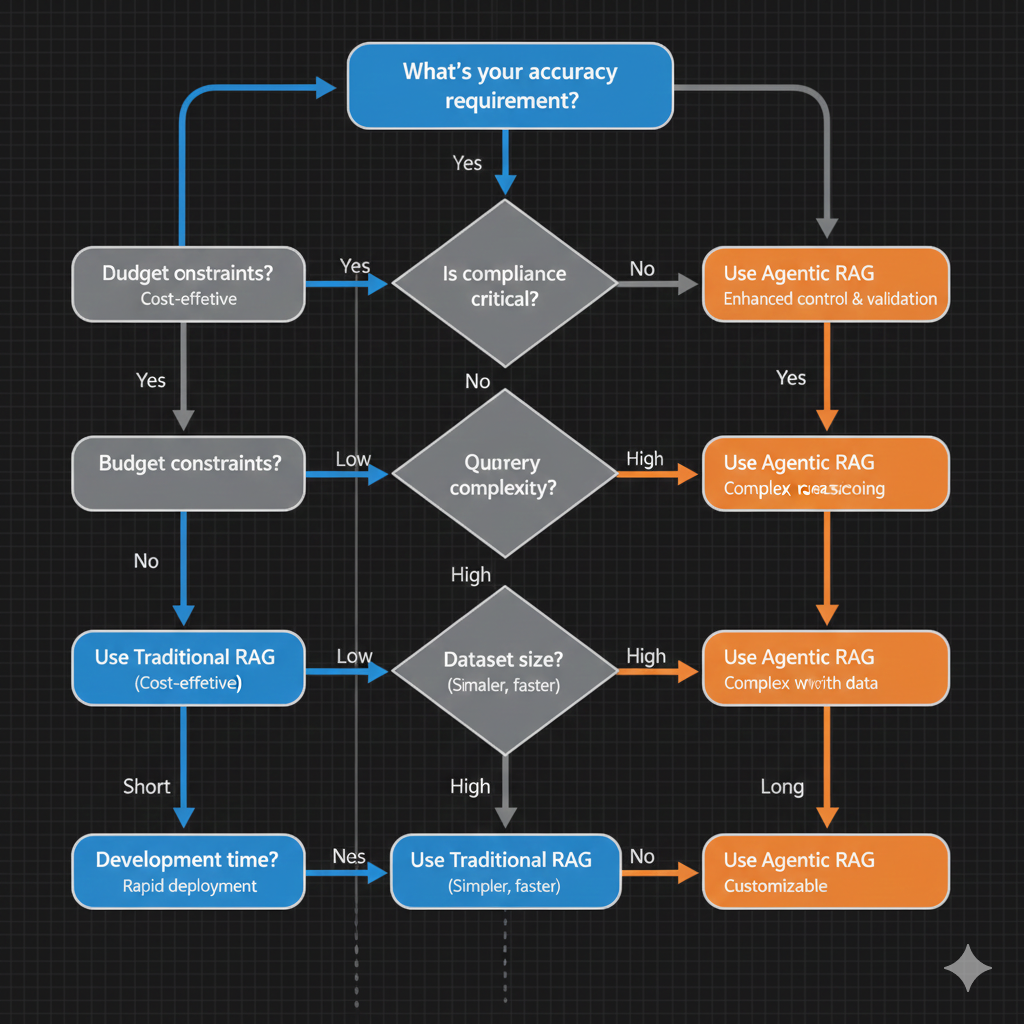
Decision Framework
Choosing the Right RAG Architecture for Your Use Case
Choose Traditional RAG If:
- Budget-Constrained Prototype
- Early-stage experiments where accuracy <90% is acceptable
- Internal tools with low stakes (e.g., employee FAQ bot)
- Small Dataset (<10,000 documents)
- Traditional RAG works fine at this scale
- Complexity of agents isn't justified
- Simple Q&A Only
- Single-hop, factual queries: "What's our refund policy?"
- No multi-hop reasoning required
- Latency Is Critical
- Need <500ms response time
- Cannot tolerate 2-second latency of CRAG loops
- Non-Regulated Industry
- No compliance requirements
- Hallucinations are annoying but not catastrophic
Choose Agentic RAG If:
- Regulated Industry (Healthcare, Finance, Legal)
- Accuracy <99% is unacceptable
- Hallucinations could trigger regulatory violations ($100K+ fines)
- Complex Queries (Multi-Hop Reasoning)
- Questions like "Find contracts depending on cut budgets approved by X"
- Require relationship traversal across documents
- Large Dataset (50,000+ documents)
- Traditional RAG's retrieval quality degrades at scale
- GraphRAG's relationship understanding becomes essential
- Structured Outputs Required
- Need tables, charts, workflows (not just text)
- A2UI generation is critical
- Compliance & Audit Trails
- Must prove AI decisions are traceable
- RBAC enforcement and PII redaction required
- Proactive Intelligence
- Want AI to flag stale content, detect conflicts, alert on issues
- Traditional RAG is reactive only
Decision Matrix
- Accuracy Requirement:
- Traditional RAG: <90%
- Agentic RAG: >99%
- Dataset Size:
- Traditional RAG: <10K docs
- Agentic RAG: >50K docs
- Query Complexity:
- Traditional RAG: Single-hop
- Agentic RAG: Multi-hop
- Budget:
- Traditional RAG: Low
- Agentic RAG: Moderate
- Compliance:
- Traditional RAG: Non-regulated
- Agentic RAG: Regulated
- Latency Tolerance:
- Traditional RAG: <500ms
- Agentic RAG: <3s
- Output Format:
- Traditional RAG: Text only
- Agentic RAG: Tables/charts
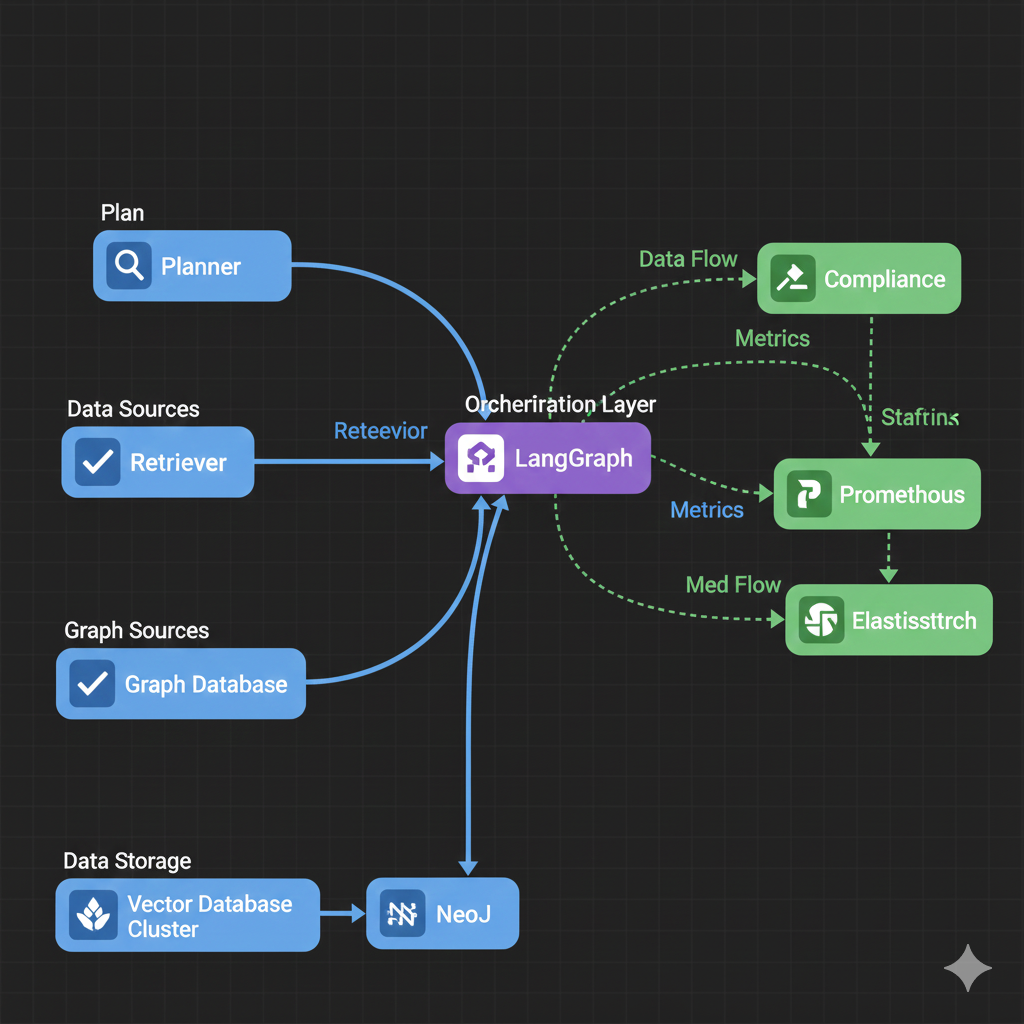
Building Agentic RAG Systems
Technical Requirements for Agentic RAG
Infrastructure
1. Vector Database
- Options: Pinecone, Weaviate, Qdrant, Milvus
- Requirements: Support for hybrid search (keyword + semantic)
- Scale: Must handle 100K+ vectors with <100ms latency
2. Graph Database
- Options: Neo4j, TigerGraph, ArangoDB
- Requirements: Efficient multi-hop traversal (BFS/DFS)
- Scale: Handle 1M+ entities and 10M+ relationships
3. Orchestration Framework
- Options: LangGraph, CrewAI, AutoGen, Semantic Kernel
- Requirements: State management, conditional edges, observability
- Docmet uses: Custom LangGraph implementation
4. Observability
- Requirements: Trace every agent decision (input state, output state, latency)
- Tools: LangSmith, Weights & Biases, custom Grafana dashboards
Development Complexity
Traditional RAG:
- Engineer Time: 2-4 weeks (experienced team)
- Skill Level: Mid-level ML engineer
- Libraries: LangChain, LlamaIndex (high-level abstractions)
Agentic RAG:
- Engineer Time: 3-6 months (experienced team)
- Skill Level: Senior ML engineer + software architect
- Libraries: LangGraph (lower-level, requires orchestration design)
- Additional Complexity: State management, CRAG loop logic, agent coordination
Cost Considerations
Inference Costs:
- Traditional RAG: ~$0.02/query (1 LLM call)
- Agentic RAG: ~$0.09/query (7 agents, 1.3 CRAG loops)
- Scaling: At 100K queries/month, difference is $2,000/mo vs $9,000/mo
Development Costs:
- Traditional RAG: $50K-$100K (2-4 weeks × 2 engineers)
- Agentic RAG: $300K-$500K (3-6 months × 3 engineers + architect)
Total Cost of Ownership (3 years):
- Traditional RAG: ~$172K (dev + inference + maintenance)
- Agentic RAG: ~$824K (dev + inference + maintenance)
ROI Justification:
- If a single compliance violation costs $500K+ (common in healthcare/finance), Agentic RAG's 99% accuracy pays for itself
- 70% time savings × 100 employees × $50/hr = $1.4M/year value
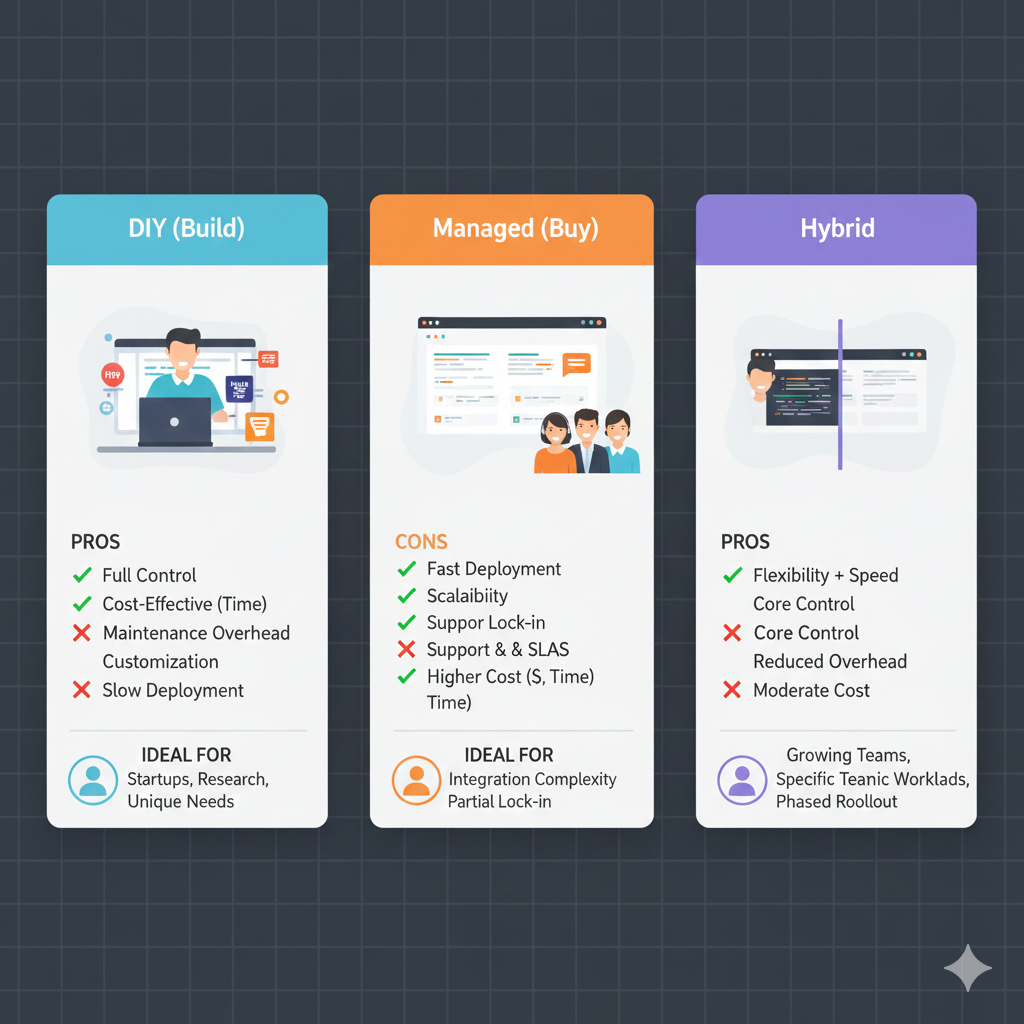
Implementation Options
Build vs Buy
🛠️ DIY Agentic RAG
Pros: full control, customization, no vendor lock-in | Cons: 3–6 months dev time, requires ML expertise, ongoing maintenance | Tools: LangGraph, LlamaIndex, Neo4j, Pinecone | Best for: teams with ML engineers and unique requirements
☁️ Enterprise-Ready Agentic RAG
Pros: deploy in 2–4 weeks, pre-built agents, SOC2 compliant, 24/7 support | Cons: higher cost than DIY, some customization limits | Includes: GraphRAG, CRAG, A2UI, compliance agents, observability | Best for: enterprises prioritizing time-to-value and compliance
🔧 Managed Core + Custom Agents
Pros: fast deployment plus custom workflows | Cons: requires coordination with vendor | Docmet offers: core platform plus custom agent development services | Best for: large enterprises with domain-specific requirements (e.g., FDA compliance)
Agentic RAG in Production
Case Study: Global Law Firm
Challenge: 500 attorneys needed to search 2M legal documents (contracts, case law, briefs) to answer client questions with verifiable accuracy.
Traditional RAG Results (Pilot):
- Accuracy: 83% (17% contained citation errors or hallucinations)
- Rejection Rate: 40% of attorneys didn't trust AI, reverted to manual search
- Risk: One incorrect citation in a court filing could cost the case
Agentic RAG Results (Docmet Implementation):
- Accuracy: 99.4% (CRAG eliminated most errors)
- Adoption: 92% of attorneys use daily
- Time Savings: 18 hours/week per attorney (previously spent on manual research)
- ROI: $12M/year value (time savings × hourly rate)
Technical Implementation
GraphRAG Knowledge Graph:
- Entities: Cases, statutes, contracts, parties, judges, precedents
- Relationships: CITES, OVERRULES, APPLIES_TO, CONFLICTS_WITH
- Example Query: "Find contracts citing cases that were overruled after 2020"
- Traditional RAG: Cannot handle this
- Agentic RAG: Traverses graph path: Contracts → CITES → Cases → OVERRULED → Date filter
CRAG Verification:
- Grader Agent scores retrieved cases for relevance to query
- If score <8/10, refines search query (e.g., adds jurisdiction constraint)
- Result: 99%+ of citations verified as accurate before presenting to attorney
Compliance Agent:
- Enforces attorney-client privilege
- Redacts confidential client information before sharing across matters
- Logs all document access for audit (bar association requirements)
Results After 12 Months
- Accuracy:
- Before (Traditional RAG): 83%
- After (Agentic RAG): 99.4%
- Attorney Trust:
- Before (Traditional RAG): 60%
- After (Agentic RAG): 92%
- Time per Research Task:
- Before (Traditional RAG): 4.5 hours
- After (Agentic RAG): 0.8 hours
- Monthly Queries:
- Before (Traditional RAG): 12,000
- After (Agentic RAG): 48,000 (4× increase due to trust)
- Compliance Violations:
- Before (Traditional RAG): 2 (PII leakage)
- After (Agentic RAG): 0
- ROI:
- Before (Traditional RAG): Break-even
- After (Agentic RAG): $12M/year positive

Common Questions from Engineering Teams
Technical FAQ
From Theory to Production-Ready AI
Building Agentic RAG from scratch takes 3-6 months. Docmet delivers production-grade, enterprise-ready Agentic RAG in 2-4 weeks. Schedule a technical deep-dive where we'll walk through our LangGraph architecture, CRAG implementation, and GraphRAG knowledge graph construction.

Technical Deep-Dives and Related Content
Learn More
